Purge and Trap: Essential Techniques in Environmental Analysis
27 May 2025
5 Mins Read
toc impalement
Assessment of the quality of natural resources is an important aspect of environmental analysis. Among many techniques, purge and trap methods are among the most precise and efficient.
This method is useful for the detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in water, as well as soil and air samples, which are necessary for environmental monitoring.
Familiarity with the fundamental concepts and applications of the purge and trap technique for volatile organic compounds testing significantly increases the effectiveness of environmental assessments.
What is Purge and Trap?
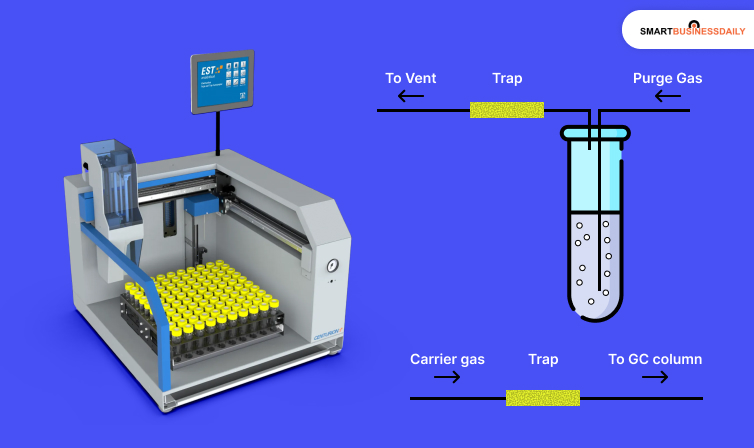
Purge and trap is a dynamic headspace extraction method for volatile organic compounds, where any purge gas, like nitrogen or helium, is passed through a sample and then carried to a trap to concentrate them.
This is globally used for environmental testing. Moreover, it performs easily with GCMS. Various EPA methods have made it compulsory to use this technique, such as 524 for drinking water, EPA 8260, 624, etc.
Purge and Trap Technique Explained
Purge and trap techniques extract VOCs present in a sample by purging it with an inert gas. Any VOCs present in the sample are transferred into a sorbent trap, where they are absorbed and retained.
Once the compounds of interest are trapped, they are subjected to thermal desorption (TD) and then analyzed through gas chromatography. This method is beneficial specifically in the detection of very low levels of VOCs, as it delivers accurate and highly reliable results.
Significance in Environmental Monitoring
Monitoring the presence of VOCs is extremely important for monitoring pollution and complying with environmental regulations. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have far-reaching consequences for health and ecosystems.
Environmental scientists can use purge and trap methods to locate where pollutants are coming from and rectify the issue. This method tracks down industrial emissions and the quality of groundwater. Moreover, it tracks the air quality emission standards.
Benefits of Purge and Trap
There are a few advantages to the purge and trap methods. These can come in handy to analyze low portions of VOCs, as some may be difficult to detect with other types of techniques.
This method is fast and needs only a small volume of the sample for preparation. Moreover, it enables very sensitive and selective research, which allows the detection of very small amounts of pollutants.
These characteristics make purge and trap a perfect fit for environmental analysis.
Water Analysis Applications
One of the main applications of purge and trap methods is water quality analysis. Using water samples, scientists can identify benzene, toluene, and other pollutants.
This is especially relevant in the context of protecting sources of drinking water and aquatic biodiversity. The adoption of these techniques for regular monitoring can prevent permanent damage to water bodies and improve public safety.
Environmental Testing of Soil and Air
Purge and trap techniques are also very important when it comes to soil and air analysis. In soil testing, they assist in identifying polluted locations and aid in clean-up activities.
This can help scientists to assess the level of contamination and come up with clean-up methods through VOC detection in soil.
These methods are also useful in air quality assessment. They determine the levels of contaminants, ensuring the air quality adheres to health standards.
Challenges and Considerations
Although the purge and trap methods have benefits, they also have drawbacks that should be considered. For accurate results, it is very important to properly calibrate the equipment and maintain it appropriately.
The choice of the sorbent material can be efficient depending on the VOCs’ trapping. Analysts need to be trained to use the equipment and interpret the data properly. Overcoming these problems will help improve the reliability of the outcomes.
Looking Ahead and Innovations
The search for new and improved methods of purge and trap analysis seems never-ending, with researchers constantly striving to develop new, more efficient ways to decouple and analyze environmental problems.
Innovations include improvements in sensitivity, analysis turnaround time, and automation. Advancements in sorbent materials and detection technologies are likely to make this method even more powerful.
All these improvements will offer greater strength as an environmental monitoring tool.
Concentrating VOCs for Analysis: Absorption Phase
A trap is a small gas chromatograph column. A trap is a small gas chromatograph column. A measurable retention volume removes the compounds that enter the trap.
Retention volume is the purge gas amount that passes through the trap before removing the analytes. Here are the requirements:
- A low temperature is used for trapping, and the retention times are quite long. They use a higher temperature for desorption, and the retention time also gets shorter. This allows quick transfer to the GC. However, the retention volume has to be perfect.
- When evolution occurs, it is known as a “breakthrough.” The volume at which this breakthrough occurs is “breakthrough volume.” Choosing the adsorbents carefully will ensure high breakthrough volume for analytes and a low breakthrough volume for water.
- The trap is packed with the weaker adsorbent on top. The weaker sorbent retains the less volatile analytes and is not desorbed by the stronger sorbent. Thus, the less volatile one fails to reach the stronger sorbent.
- The more volatile analytes reach the stronger sorbent. Because of their volatility, these analytes are desorbed efficiently. Backflushing the trap carries out the desorption and ensures that the heavier analytes don’t come in contact with the stronger sorbent.
Conclusion
The purge and trap technique is a highly competent method in environmental analysis for determining VOC concentrations in different matrices. They are used for testing water, soil, and air, which guarantees the protection of natural resources and public health.
Through tackling existing issues and potential innovations on the horizon, environmental scientists can continue to enhance the efficiency of these techniques.
Purge and trap remains a vital part of modern environmental assessment, and gaining a clear understanding of the methodology is key to its accuracy and reliability.
Also Read:

















Comments Are Closed For This Article